Understanding Piles: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Introduction
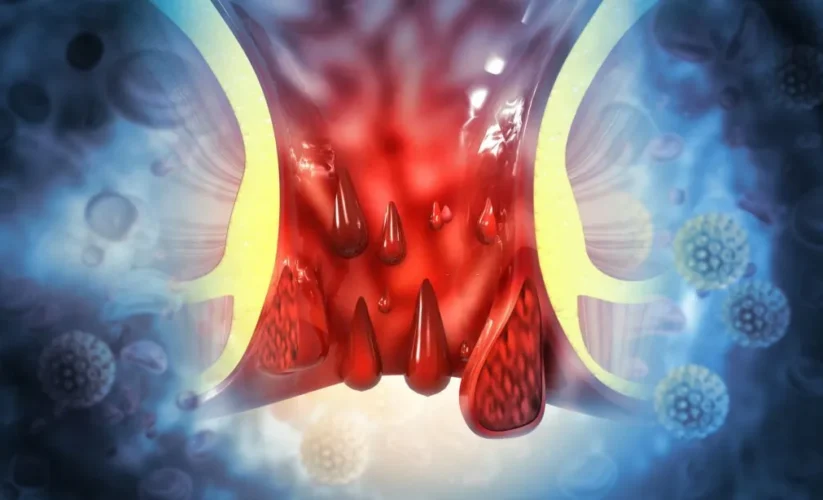
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are swollen veins in the lower rectum or anus. They can cause discomfort, itching, and bleeding, affecting millions of people worldwide. While it is a common condition, many are still unaware of its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. In this article, we will explore piles in detail, their historical context, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and various management approaches, including medical, surgical, and home remedies.
Historical Background
Hemorrhoids have been recorded in ancient medical literature dating back to Egyptian manuscripts around 1700 BC. The ancient Greeks also mentioned this condition, with Hippocrates proposing ligation techniques for treating hemorrhoids. Despite advancements in medical science, piles remain a prevalent condition, affecting both men and women.
What Are Piles?
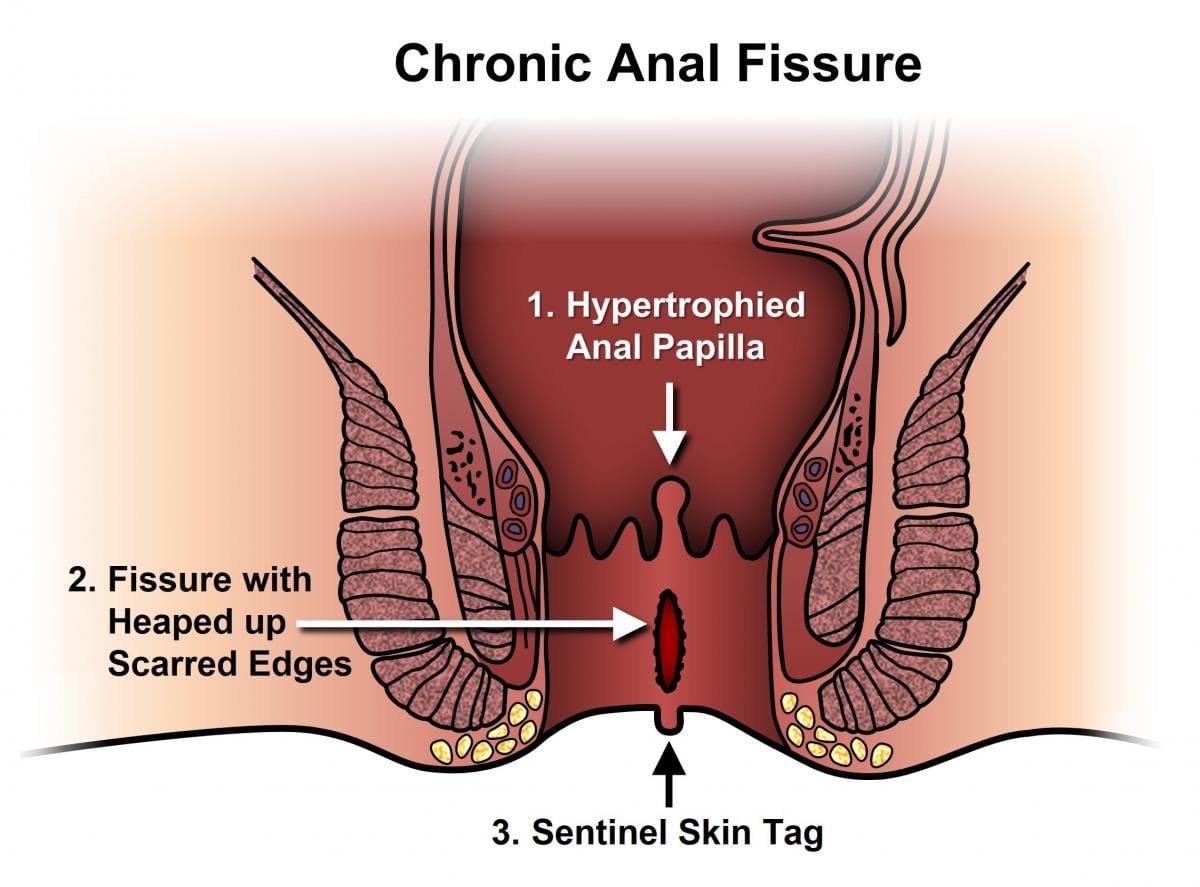
Piles or hemorrhoids refer to swollen veins in the rectal area. They are classified into two types:
Internal Piles: Located inside the rectum, usually painless but may cause bleeding.
External Piles: Located under the skin around the anus, often causing pain, itching, and bleeding.
Degrees of Piles:
Hemorrhoids are classified into four degrees based on their severity:
- FirstDegree Hemorrhoids: These are internal hemorrhoids that may bleed but do not prolapse (come out of the anal canal). They are not visible externally.
- SecondDegree Hemorrhoids: These hemorrhoids prolapse out of the anal canal during bowel movements but retract back inside automatically. They may cause bleeding and discomfort.
- ThirdDegree Hemorrhoids: These hemorrhoids prolapse out of the anal canal during bowel movements and do not retract automatically. They need to be manually pushed back inside. These can cause pain, bleeding, and discomfort.
- FourthDegree Hemorrhoids: These are the most severe form. They are permanently prolapsed and cannot be pushed back inside the anus. They can lead to significant pain, bleeding, and complications like thrombosis or ulceration.
Symptoms of Piles
The symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition:
Bright red blood during bowel movements
Itching or irritation in the anal region
Pain or discomfort, especially during bowel movements
Swelling around the anus, something coming out of anus.
A lump near the anus, which can be painful or sensitive
Causes of Piles
Several factors contribute to the development of piles, including:
Chronic Constipation: Straining during bowel movements increases pressure on rectal veins.
Pregnancy: Increased pressure in the pelvic area can lead to piles in pregnant women.
Obesity: Being overweight increases pressure on the rectal veins.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Prolonged sitting can contribute to the condition.
Family History: A genetic predisposition to piles can make some individuals more susceptible.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis is usually made through a combination of medical history and physical examination. A doctor may perform a digital rectal exam (DRE) or use an anoscope to examine the rectal area. For internal hemorrhoids, procedures like sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy may be recommended to rule out other causes of rectal bleeding.
Management of Piles
Medical Treatment
Mild cases of piles can often be managed with lifestyle changes and medications:
Medications: Overthecounter creams, ointments, and suppositories can relieve pain and itching. Antiinflammatory medications may also be prescribed to reduce swelling.
Laxatives: Stool softeners or mild laxatives can prevent constipation and reduce strain during bowel movements.
Home Remedies for Piles
HighFiber Diet: Consuming foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can ease bowel movements.
Warm Sitz Baths: Sitting in warm water for 1015 minutes several times a day can relieve pain and itching.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps soften stools and prevent constipation.
Avoid Straining: Relax and avoid excessive straining while passing stools.
When Is Surgery Needed?
Surgery is recommended if piles do not respond to conservative treatment, causing persistent pain, bleeding, or prolapse.
Surgical Options for Piles
Several surgical procedures are available based on the severity of the condition:
Rubber Band Ligation: A rubber band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid, cutting off blood flow and causing it to shrink.
Injection Sclerotherapy: A chemical solution is injected to shrink the hemorrhoid.
Hemorrhoidectomy: A surgical procedure to remove large, prolapsed hemorrhoids.
Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: A procedure to reposition the hemorrhoid and cut off its blood supply.
Laser Treatment: A minimally invasive procedure using laser energy to treat hemorrhoids.
How to Contact Us
For further inquiries, appointments, or consultations, visit: (https://www.surgeondrimtiazhussain.com). You can also consult with Surgeom Dr. Imtiaz Hussain online or in person. For online consultations, please follow these steps:
- Send Your Reports: Send any previous reports, prescriptions, and pictures of the affected area.
- Book Your Appointment: Transfer Rs. 3000 via JazzCash or bank transfer, and you will receive a detailed audio consultation with Dr. Imtiaz.
Conclusion
Piles are a common but manageable condition. Understanding their symptoms and causes can help you take preventive measures. If conservative treatments are not effective, surgical intervention may be necessary. Our experienced team at surgeondrimtiazhussain.com is here to help you on your journey to better health.
By following the right treatment plan and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can effectively manage and even prevent piles.