Hernia: A Complete Guide to Understanding, Diagnosing, and Treating the Condition
A hernia is a common condition affecting many people worldwide. Although the term is often heard, not everyone fully understands what a hernia is, its potential risks, or the treatment options available. This article delves deep into the world of hernias, exploring the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatments, both surgical and nonsurgical.
What Exactly Is a Hernia?
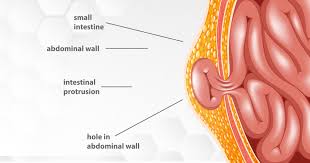
A hernia occurs when an organ or fatty tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. It commonly develops in areas like the abdomen, groin, or near surgical scars. Hernias can be uncomfortable and, in some cases, lifethreatening if left untreated.
Historical Background: The Evolution of Hernia Treatment
The concept of hernias dates back to ancient Egypt and Greece. Early physicians recognized hernias as a protrusion of the intestines through a weak spot and developed rudimentary techniques to manage them. As medical knowledge advanced, so did surgical techniques, leading to safer and more effective treatment options today.
Types of Hernias
- Inguinal Hernia: The most common type, occurring in the groin area.
- Umbilical Hernia: Appears near the navel and is common in infants and pregnant women.
- Incisional Hernia: Develops at the site of a previous surgical incision.
- Hiatal Hernia: Occurs when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity.
Symptoms of a Hernia
Recognizing the symptoms of a hernia can help you seek medical advice early on. Some common signs include:
Bulge or Lump: Noticeable swelling or lump in the affected area, which may disappear when lying down.
Pain or Discomfort: Worsened by activities like lifting, bending, or coughing.
Weakness or Pressure: Feeling of heaviness or weakness in the abdomen or groin.
Burning Sensation: A mild burning sensation at the site of the bulge.
Why Do Hernias Occur?
Hernias often result from a combination of muscle weakness and strain. Some of the common causes include:
Heavy Lifting: Strain from lifting heavy objects without proper support.
Obesity: Excess weight can put added pressure on the abdominal wall.
Chronic Coughing: Persistent coughing can lead to hernias over time.
Previous Surgeries: Scar tissue and weakened muscles from surgeries may create a risk for hernia formation.
How Is a Hernia Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination to detect any bulges. In some cases, imaging tests like ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs may be recommended to assess the extent of the hernia and plan treatment accordingly.
NonSurgical Management of Hernias
While surgery is the definitive treatment for most hernias, certain cases can be managed without surgery:
Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding heavy lifting, and treating chronic coughs.
Hernia Belts or Trusses: These can provide temporary relief by supporting the affected area.
Medications: Pain relievers or drugs to address the underlying causes, like acidreducing medications for hiatal hernias.
Home Remedies and SelfCare
Home care can play a vital role in preventing hernias from worsening:
Eat HighFiber Foods: To prevent constipation and reduce abdominal strain.
Exercise Safely: Focus on lowimpact exercises to strengthen core muscles.
Stop Smoking: This can reduce chronic coughing, which is a significant risk factor.
When Is Surgery Necessary?
Surgery is essential if:
The hernia is causing severe pain or discomfort.
There is a risk of strangulation or obstruction of the intestine.
The hernia is growing in size over time.
Surgical Options for Hernia Repair
- Open Hernia Repair: Involves making an incision to push the protruding organ back in place and reinforcing the weakened area.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive procedure using small incisions and a camera to guide the surgeon. This method usually results in faster recovery times.
- RoboticAssisted Surgery: Offers increased precision and flexibility, especially for complex hernias.
PreOperative Considerations: What to Know Before Surgery
Necessary Tests: Blood tests, imaging scans, and cardiac evaluations to ensure fitness for surgery.
Fasting Guidelines: Usually, patients must avoid eating for 6 to 8 hours before surgery to minimize anesthesia risks.
How Long Does a Hernia Surgery Take?
Inguinal or Umbilical Hernia Repair: Generally takes about 30 to 45 minutes.
Incisional Hernia Repair: Depending on complexity, it may require 45 to 60 minutes.
PostSurgery: What to Expect and Recovery Guidelines
Hospital Stay: Most hernia surgeries are done on an outpatient basis, but some patients may need a short hospital stay for monitoring.
Resuming Diet: Start with liquids and gradually transition to solid foods within 24 hours.
Activity Levels: Gentle walking is encouraged the same day of surgery, but avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activities for at least 4 to 6 weeks.
When Can You Return to Work or Daily Activities?
Depending on the type of hernia and surgery performed, most patients can return to light activities within 1 to 2 weeks and resume full activities in 4 to 6 weeks. For patients with desk jobs, returning to work might be possible in as little as a week.
How to Ensure a Full Recovery
The complete recovery time for hernia repair varies:
Inguinal or Umbilical Hernias: Approximately 3 to 4 weeks.
Incisional Hernias: Around 6 weeks.
FollowUp and PostOperative Care
At (https://www.surgeondrimtiazhussain.com), our followup care ensures a comprehensive recovery. Local patients are encouraged to visit the hospital for checkups. Both national and international patients can stay in contact through WhatsApp for updates on wound healing and further advice. Dr. Imtiaz Hussain personally monitors each case for optimal outcomes.
Contact Us for Expert Advice
If you are experiencing symptoms of a hernia, don’t hesitate to seek help. You can contact us for an appointment or online consultation. Simply send your reports and images for a preliminary assessment, and Dr. Imtiaz Hussain will provide you with a tailored treatment plan.
Conclusion
A hernia is a manageable condition if diagnosed and treated promptly. With various surgical options available today, it is possible to regain your health and quality of life. Stay informed, take preventive measures, and consult a specialist for expert advice.
Take control of your health and reach out to us today if you have concerns about a hernia or need expert advice on managing the condition.